Externally, GPU servers are very similar to regular PCs and workstations. However, this is where their similarities end. In terms of capabilities and architecture, these are completely different equipment. Let’s tell you how exactly GPU servers differ from standard computers.
Main purpose
- gaming and streaming;
- programming;
- surfing the internet;
- working with text documents;
- work in creative programs (video editing, graphic design, 3D modeling, architectural design, etc.).
- machine learning;
- working with neural networks;
- rendering of complex projects;
- Big Data analysis;
- computation of simulations (CFD, FEA).
Despite the external similarity with regular PCs, servers with video cards significantly surpass them in performance and hardware.
Main components and subsystems
Central Processing Units
Personal computers are usually equipped with Intel Core and AMD Ryzen processors. These are energy-efficient solutions with a small number of cores.
- increased reliability;
- increased cache volume;
- higher heat generation;
- a large number of cores and threads;
- advanced instructions for AI tasks;
- support for more PCI-E lanes;
- the ability to work with huge amounts of ECC memory.
Server processors are designed for 24/7 load and are significantly ahead of desktop models in terms of computing capabilities.

Graphic accelerators
Gaming PCs and workstations come with NVIDIA GeForce and AMD Radeon graphics cards, which handle games and basic rendering well.
- specialized drivers;
- increased video memory;
- support for FP16, FP32, TF32, INT8, INT4 formats;
- high performance in tensor operations (FLOPS);
- NVLink and NVSwitch technologies for combining multiple GPUs;
- the ability to divide a single graphics processor into multiple logical units using the Multi-Instance GPU feature.
Server graphics accelerators are designed for professional tasks and support many technologies that are not needed by ordinary users.

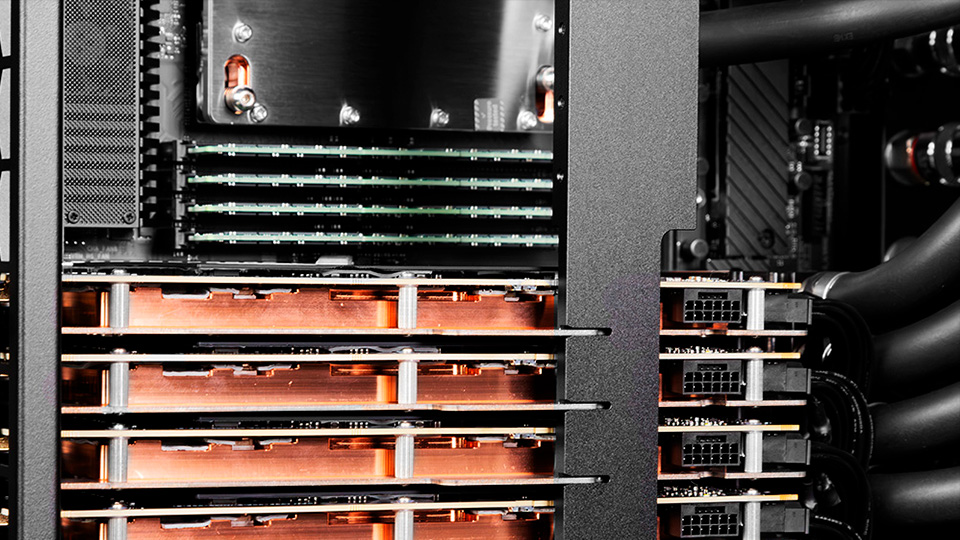
RAM
Standard PCs come with 16-64 GB of RAM. Servers come with 64 GB to several terabytes. Such a large amount is needed for complex tasks. For example, for machine learning or rendering resource-intensive projects.
- NUMA architecture;
- ECC (Error Correction Code);
- backup technologies (memory sparing, memory mirroring).
The listed technologies increase operational stability and reduce the number of random equipment failures.
In addition, the server memory operates in 4-, 6-, and 8-channel mode, which provides higher throughput. This is especially important when processing large amounts of data, which is often required for data centers and scientific computing.
Another feature is the ability to “hot-swap” memory modules without having to turn off the equipment.
File storage
Gamers and professionals do not need a large file storage. One or two small storage drives are enough for them. The exception is video editors. They need to store “sources” on their PCs, which can weigh tens of terabytes. In all other cases, a large file storage is unnecessary. That is why workstations and gaming PCs do not have many storage drives. In most cases, they are redundant.
GPU servers, on the contrary, are equipped with large arrays of storage devices to store “heavy” data. This could be AI algorithms, high-resolution video files, scientific calculations, and so on. In addition, storage devices in servers are combined into RAID arrays to increase throughput and backup.

Cooling system
The cooling system in servers is slightly different from regular PCs due to the shape of the cases. They also use air fans, but turbine type. Such coolers “pull” air through the entire case and cool all components evenly. In addition, fans in servers are installed only on two sides: the front for intake and the back for exhaust. There are no fasteners for coolers on the top and bottom, like in regular PCs.
GPU servers are often designed based on custom liquid cooling systems, where water blocks are installed on all components and connected with tubes. Otherwise, it may not be possible to achieve low operating temperatures with several graphics accelerators. Custom liquid cooling systems are rarely installed in regular PCs with one video card. This is mainly a solution for enthusiasts.
Power supply
Gaming, office and professional computers are equipped with power supplies of the ATX, SFX, FlexATX and TFX form factors. Their power is 400-700 W. Only the most productive PCs are equipped with power supplies with a power of 1000-1500 W.
- Redundant Power Supply Units (RPSU);
- Hot-Swappable Power Supplies;
- Server-grade PSU.
These PSUs have a modular design, a narrow case, and a handle for extraction on the front panel. They also connect to the server board directly, without using cables. Several power supplies can be installed in one GPU server, since graphic accelerators consume a lot of energy.
Upgrade and Scaling
- InfiniBand – ultra-fast network (Up to 400 Gbps);
- RDMA – direct access to the memory of another server;
- SLURM is a cluster task scheduling system;
- Kubernetes – automatic management of containerized applications;
- NVIDIA Bright Cluster Manager is a comprehensive software for managing, monitoring and scaling clusters.
These technologies allow you to combine servers into clusters, that is, into a single computing system. In other words, they allow you to create one, but very powerful, computer from several computers.
Software and management
Windows operating systems are installed on regular computers and workstations. Much less often – Linux. Other operating systems are used on servers. Most often, these are Linux distributions: Ubuntu Server, RHEL and Debian. Also, the programs that we are used to using are not installed on servers. Other software is used there. For example, Docker and Singularity for containerization, NVIDIA CUDA Toolkit and Triton Inference Server for the GPU scheduler, Prometheus and Grafana for monitoring.
Differences between a GPU server and a regular PC: summary
- Purpose.
Unlike a general-purpose computer, a GPU server is designed for demanding, highly specialized tasks. - Processor.
The servers use Intel Xeon, AMD EPYC and AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors with a large number of cores, cache memory and ECC support. - Video cards.
The servers are equipped with professional accelerators with large memory capacities, such as NVIDIA A100, H100, L40 and RTX A6000. - RAM.
Servers are equipped with RAM that supports ECC, NUMA and backup, and its volume can reach several terabytes. - File storage.
Instead of one or two drives, as in conventional PCs, servers use arrays of multiple HDD and SSD disks. - Cooling system.
Server equipment heats up more than in regular PCs, so custom liquid cooling systems and turbines are used for cooling. - Power supply.
Narrow power supplies with a capacity of up to 3000 W are installed in servers. In some configurations, several of them are installed. - Upgrade options.
To increase performance, servers can be clustered and connected via a high-speed network. - Software.
Server equipment with video cards runs on Linux distributions, not the usual Windows OS.

